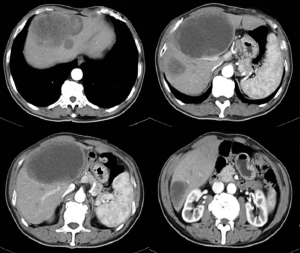
Multiple liver lesions with dormant submandibular gland nodule
A 73-year-old male was admitted 1 month after detection of multiple liver lesions. He did not complain of any symptoms. Physical examination showed a palpable, hard, tender nodule measuring 4 cm × 4 cm in the right submandibular gland, and skin rash and swelling of his external genitalia. His abdomen was soft, with no signs of peritoneal irritation and no palpable mass. He denied any history of hepatitis or alcohol abuse. Laboratory test results showed a normal blood cell count, normal liver and lung function, and normal coagulation. Serum tumor markers were within the normal range. Testing for infectious disease markers showed a positive rapid plasma reagin titer of 1:16 and a positive Treponema pallidum antibody test. Liver ultrasonography showed several lesions with mixed echogenicity (largest lesion: 15 cm × 12.7 cm × 10.6 cm), with irregular anechoic areas (largest size: 12.8 cm × 9.6 cm × 7.5 cm). Computed tomography showed multiple intrahepatic cystic masses, with marked peripheral enhancement. Surgical exploration revealed multiple huge solid/cystic masses in the liver. The largest mass was in the middle lobe, which oppressed the first porta hepatis and was close to three major hepatic veins. The large masses in the middle lobe and the lesions in segments IV, VI and VII were resected. Pathological examination showed adenocarcinoma, which was considered to be of salivary gland origin. Based on the clinical manifestations and positron emission tomography findings, the patient was diagnosed with carcinoma of the submandibular gland with liver metastases. After treatment of his syphilis, he underwent radical resection of the right submandibular gland tumor. He was on chemotherapy following the surgeries. New liver metastases were detected 9 months after the hepatectomy, and he is receiving RFA now.
Acknowledgements
Disclosure: The authors declare no conflict of interest.